Getting started
-
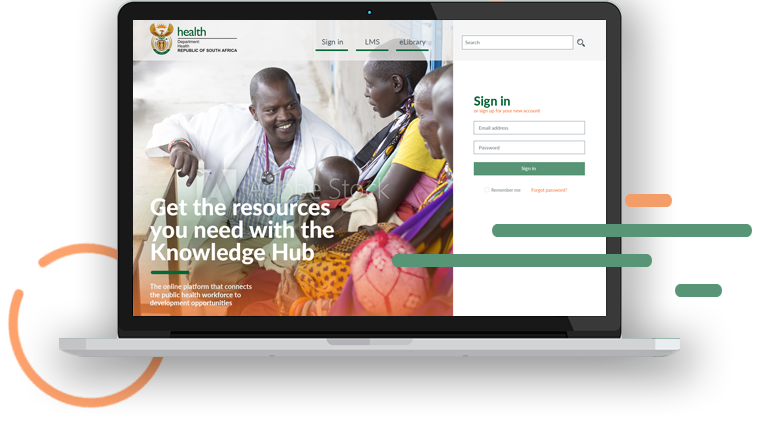
Simple sign up
- Visit the Knowledge Hub on your computer, tablet or phone.
- Click the Sign up button. Follow the simple process to create your personal profile. You will need your PERSAL and ID numbers, facility name and job role profile.
- Next time you visit, simply log in with your chosen username and password.
-
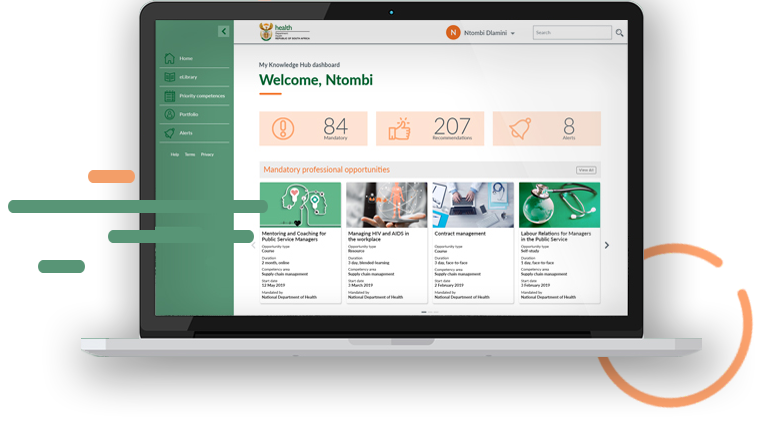
Start your unique development journey
- Choose priority competencies to streamline and customise your dashboard.
- Customise your KH dashboard feeds based on your CPD opportunity preferences.
- View and manage bookmarked CPD opportunities.
- Access a personalised portfolio of current and completed professional development opportunities.
- Update your personal information and preferences at any time in the future as your needs change.
-

Personalise your dashboard
- Based on your role profile and facility, the Hub will identify mandatory and recommended opportunities for you.
- Access a searchable catalogue of all national and provincial Department of Health development opportunities available on the Knowledge Hub.
- Bookmark identified opportunities to keep a record of those you would like to take up at a later date.
- Enrol in opportunities and keep a printable record of opportunities you have completed.
- Access an eLibrary of curated policies, guidelines and standard operating procedures.
- Receive Knowledge Hub email alerts targeted specifically for you.
